

Let's move on to finding out how this table can be used to help us graph out linear equations. One column lists the x values, and one column lists the corresponding y values. You'll need to use at least 2 sets of points to graph out a linear equation, but you will usually do more in a table of values.Ī table of values has two columns. It's a place for you to jot down the answers you get when you find the value of x and y.
A table of values, as its name suggests, is a graphical way to determine the values that will be used to create your graph. When we have to graph out a linear equation, you'll start by creating a table of values.
#Onto vs one to one graph how to#
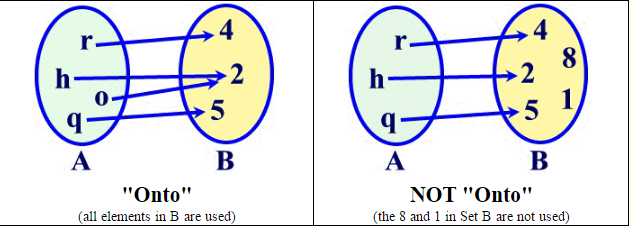
You probably know how to read a linear equation graph, but how do we go about plotting out a linear equation onto a coordinate plane? It turns out it's actually not that hard! The first step is learning how to do a table of values. If f and g are onto then the function $(g o f)$ is also onto.Ĭomposition always holds associative property but does not hold commutative property.A linear equation is an equation that has two variables that when graphed gives us a straight line. If f and g are one-to-one then the function $(g o f)$ is also one-to-one. Hence, $(f o g)(x) \neq (g o f)(x)$ Some Facts about Composition This is a function from A to C defined by $(gof)(x) = g(f(x))$ Example Two functions $f: A \rightarrow B$ and $g: B \rightarrow C$ can be composed to give a composition $g o f$. ExampleĪ Function $f : Z \rightarrow Z, f(x)=x+5$, is invertible since it has the inverse function $ g : Z \rightarrow Z, g(x)= x-5$.Ī Function $f : Z \rightarrow Z, f(x)=x^2$ is not invertiable since this is not one-to-one as $(-x)^2=x^2$. The function f is called invertible, if its inverse function g exists. The inverse of a one-to-one corresponding function $f : A \rightarrow B$, is the function $g : B \rightarrow A$, holding the following property − Since f is both surjective and injective, we can say f is bijective. So, $x = (y+5)/3$ which belongs to R and $f(x) = y$. Prove that a function $f: R \rightarrow R$ defined by $f(x) = 2x – 3$ is a bijective function.Įxplanation − We have to prove this function is both injective and surjective. $f : R \rightarrow R, f(x) = x^2$ is not surjective since we cannot find a real number whose square is negative.Ī function $f: A \rightarrow B$ is bijective or one-to-one correspondent if and only if f is both injective and surjective. $f : N \rightarrow N, f(x) = x + 2$ is surjective. This means that for any y in B, there exists some x in A such that $y = f(x)$. Equivalently, for every $b \in B$, there exists some $a \in A$ such that $f(a) = b$. $f: R\rightarrow R, f(x) = x^2$ is not injective as $(-x)^2 = x^2$Ī function $f: A \rightarrow B$ is surjective (onto) if the image of f equals its range. $f: N \rightarrow N, f(x) = x^2$ is injective. $f: N \rightarrow N, f(x) = 5x$ is injective. This means a function f is injective if $a_1 \ne a_2$ implies $f(a1) \ne f(a2)$. Injective / One-to-one functionĪ function $f: A \rightarrow B$ is injective or one-to-one function if for every $b \in B$, there exists at most one $a \in A$ such that $f(s) = t$. ‘x’ is called pre-image and ‘y’ is called image of function f.Ī function can be one to one or many to one but not one to many. X is called Domain and Y is called Codomain of function ‘f’.įunction ‘f’ is a relation on X and Y such that for each $x \in X$, there exists a unique $y \in Y$ such that $(x,y) \in R$. Function - DefinitionĪ function or mapping (Defined as $f: X \rightarrow Y$) is a relationship from elements of one set X to elements of another set Y (X and Y are non-empty sets). The third and final chapter of this part highlights the important aspects of functions. Functions find their application in various fields like representation of the computational complexity of algorithms, counting objects, study of sequences and strings, to name a few. A Function assigns to each element of a set, exactly one element of a related set.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
